The 7 Foremost Methods of 3D Rapid Prototyping Services
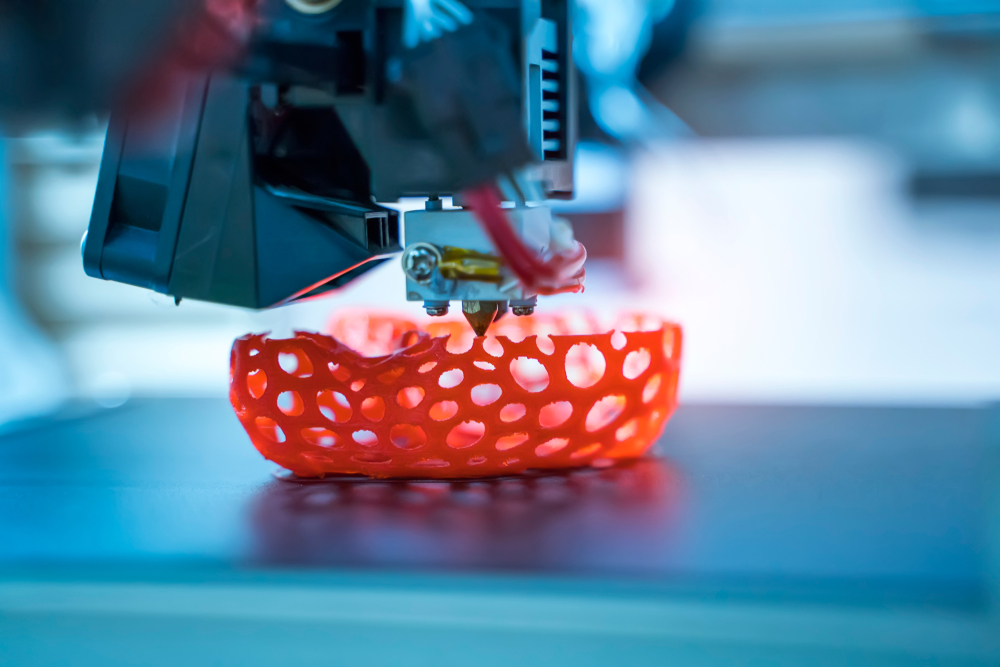
Rapid Prototyping services have evolved from head to toe since their inception in the 1980s. Engineers are constantly working towards new and simpler processes and methods. While some of the rapid prototyping methods are suitable for consumer applications and some for industrial environments. Here are the top 7 rapid prototyping services with their strengths and weaknesses to opt for your next project:
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography is the oldest and most used commercial 3D printing process in the engineering segment. In this process, manufacturing engineers equip UV light to transform the photosensitive liquid into 3D tangible plastics. The engineers derive 2-dimensional cross-sections from the 3D CAD model with the help of a software file format known as .stl. Because of the same reason, .stl is a default computer language present in modern 3D printers. Despite it’s the oldest technology, it still has the competency to develop complex geometrical shapes and high-quality prototypes.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS is an additive manufacturing process, patented by Carl Deckard in the 1980s that consumes a high-power laser to fuse powdered thermoplastics while developing parts. The parts are engineered on a build plate, one layer at a time. Unlike other rapid prototyping services methods, SLS supports all sides of the powder media and thereby doesn’t require additional structures. Moreover, it helps engineers to work on complex geometries like internal lattice structures. SLS is suitable for both plastic and metal prototypes.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Be it automotive or consumer goods manufacturing domain, FDM is the top choice of engineers when using a thermoplastic filament to develop 3D objects. This rapid prototyping method is easy-to-use, flawless, economical, and can offer various colors and types of plastic integrated with a single build. Moreover, it is safer to be used by even kids as well in schools or institutes. Another biggest benefit that tag along with FDM is scalability which makes it the best fit for developing prototypes and other engineering models.
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
SLM is one of the forms of powder bed fusion, an engineering process that needs carefully controlled conditions. To liquefy and fuse metallic powders, this process requires a high-power laser. Stainless steel, maraging steel Titanium, and cobalt chrome are the common metal powders.
Engineers especially prefer SLM for developing complex and chic parts of the highest durability and strength. However, the process is comparatively expensive and therefore is only handled by expert engineers. But, the outputs are ideal when creating parts for perceptive areas like automotive, aerospace, defense, and health.
Laminated Object Manufacturing
 +91-120-4736400
+91-120-4736400 info@sphinxworldbiz.com
info@sphinxworldbiz.com